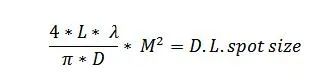Understanding the Key Advantages of Beam Shaping in Laser Processing Applications
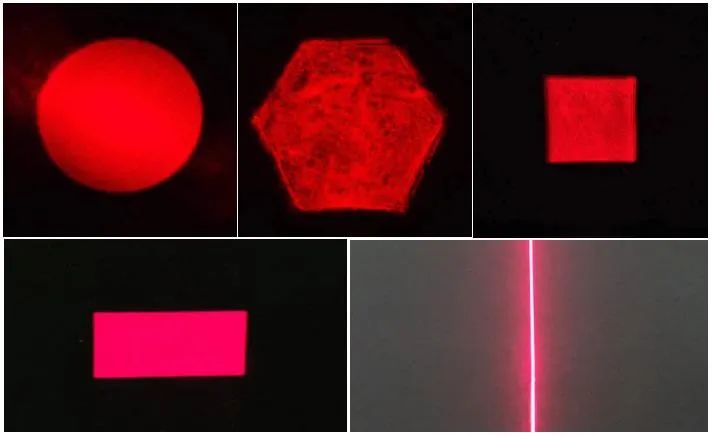
In laser industrial manufacturing, the Gaussian like beam of laser is usually converted into a flat top beam. The characteristic of a flat top spot is that the energy at the top is uniform and the boundary is very sharp, that is, the "transition zone" is short, and a steep curve of 90% to 10% of the laser energy on the spot can produce obvious laser boundaries, clearly distinguishing between the laser processing area and the unprocessed area.Therefore, flat top light is very suitable for various laser processing applications, achieving efficient and high-precision requirements.
The beam shaper can convert Gaussian incident laser beams into circular, rectangular, square, straight, or other custom shapes. Even if the pulse energy is changed, the flat top spot can maintain the same effective area.The flat spot generated by the beam shaper is commonly used in laser processing to prevent overexposure or underexposure in specific areas.
The typical applications of beam shaper include: laser welding, laser cutting, laser marking, laser printing, laser drilling, laser slicing, laser ablation, laser melting, laser rapid prototyping, laser 3D printing and other laser lens optical path design and production manufacturing, as well as miniLED welding maintenance, LDI shaping light source, laser medicine, aesthetic laser (landscape) and entertainment laser.
technology
popularization of science
Q: What is beam shaping? How to achieve it? What are the advantages?
Beam shaping refers to the use of beam shaping lenses, lenses, microlenses, or fibers of different shapes to achieve uniform effects on the light spot.
It mainly uses a diffractive optical element to convert Gaussian incident laser beams into circular, rectangular, square, straight or other custom shapes.
By shaping the laser beam into various energy distributions specific to specific treatments and processes, the power utilization and laser processing efficiency of laser manufacturing have been improved, achieving higher laser processing efficiency and quality.
The specific spot effect is shown in the following figure:
Schematic diagram of laser optical path:
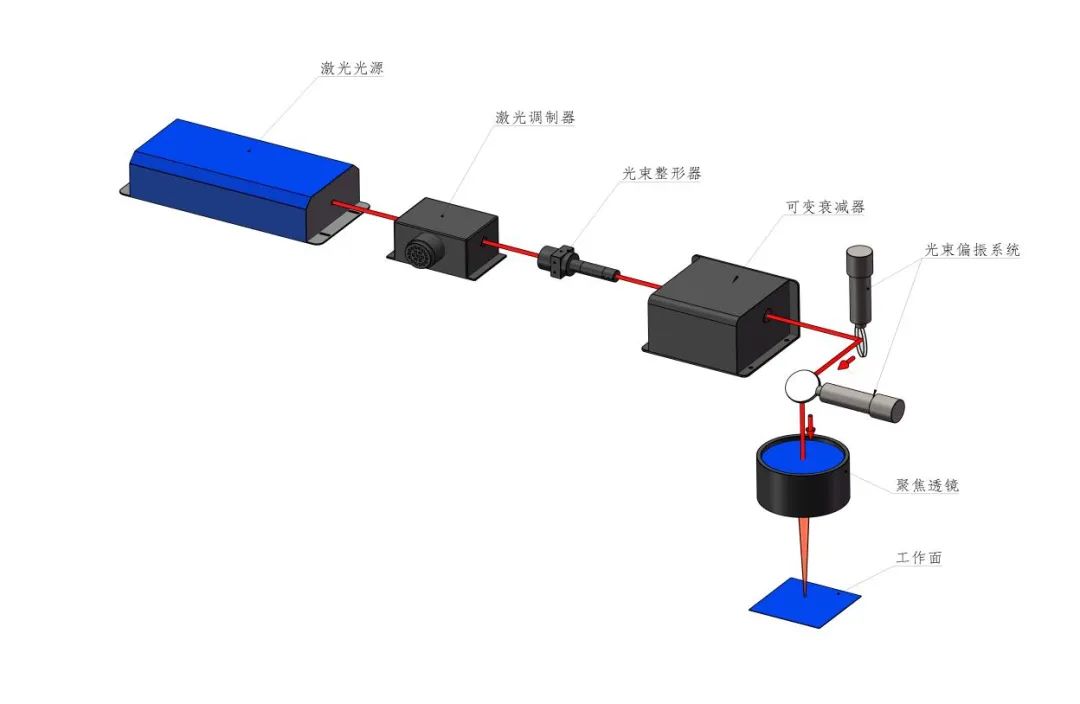
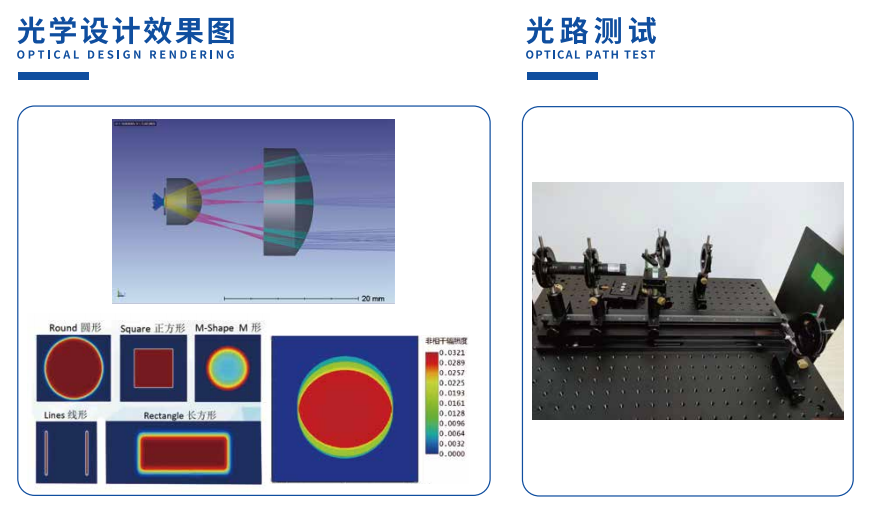
The principle of using a beam shaper
The most classic structures in beam shaper applications include laser sources, beam shaper components, focusing optical components, and working surfaces.
Each flat top beam shaper is designed with a specific set of optical system parameters:
1. Incident laser wavelength 2. Working distance (EFL) 3. Incident laser beam parameters (D) 4. Output spot size (d)
Precautions and limitations for using beam shaping
In order to achieve high-quality flat top spot performance, the incident laser needs to be collimated and the mode should be single mode M ²< 1.3. If M ² As the value increases, the effect of the resulting flat spot becomes worse.
All apertures in the beam path must be at least twice the size of the incident laser beam (2.5 times larger is optimal), as too small apertures can create interference patterns or ripples on the output spot. These apertures typically include flat mirrors (used for beam folding or scanning), beam expanders, laser beam splitters, and focusing optical devices.
All optical components in the beam path should have high quality, i.e. low aberration levels, to avoid increasing wavefront errors and reducing flat spot performance.
When designing the required output flat top light size, the diffraction limit (DL) should be considered, which is the physical optical limit of the minimum output spot size. That is, if the beam shaper is removed from the system, the ideal output spot size is the size of the diffraction limit spot. Based on experience, the output flat top spot size of the beam shaper is at least 1.5 times the diffraction limit spot size defined by the following formula (forM ²=1).
The formula for diffraction limit spot size:
Among them: L is the effective focal length of the focusing optical device, λ Is the wavelength of the incident laser, D is the size of the incident laser beam,M ²The quality parameters of the incident laser beam.
Quality factor of beam shaper
Some basic rules for the effect of a beam shaper:
-The size of the flat top spot cannot be smaller than the diffraction limit spot size.
-The factor between the size of the beam shaper and DL determines the quality and efficiency of the beam shaper. A larger factor can make the edges sharper.
-The transition zone of the beam shaper cannot be less than 0.5 DL, usually about 1-10 DL.
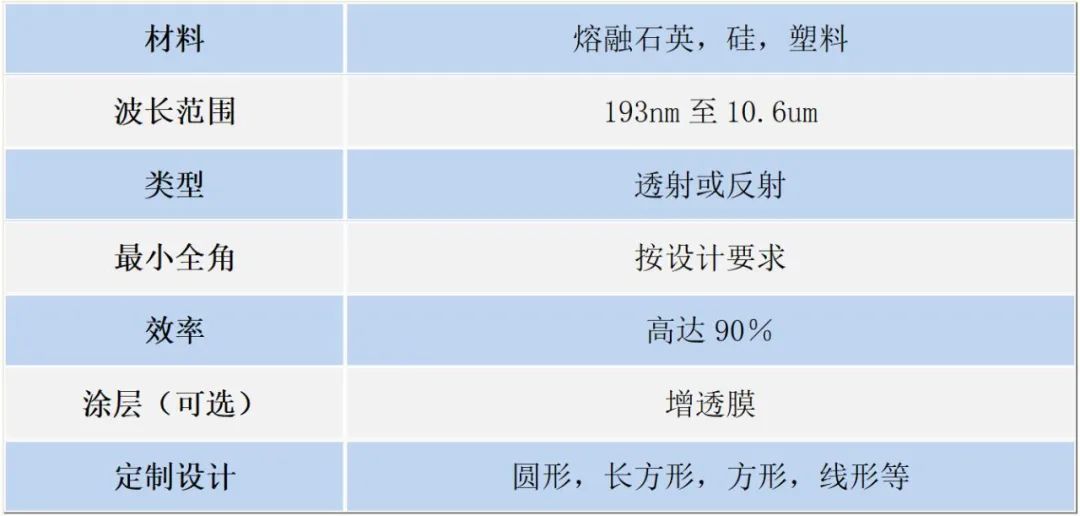
General specifications of beam shapers
Table 1
Tolerance table for typical beam shapers
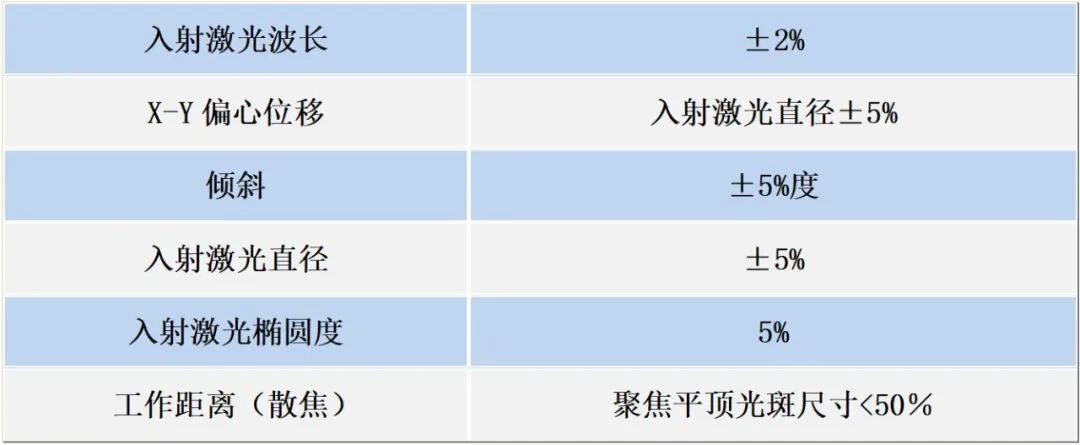
Table 2
Source: Jiamei Electronics
Laser technology has penetrated into various industrial application fields."Full session 2023 Optoelectronic Technology Expo"Simultaneously held with the Global Digital Economy Conference, sharing over 100000 professional audiences, optimizing display structure, and segmentingLaser exhibition area and new display exhibition areaBy achieving centralized display and multi-level communication in the fields of laser, display, and digital economy, our network and channels have been greatly expanded, containing unlimited business opportunities.
Industry leading new product launch,Laser precision machining exhibition area and new display exhibition areaTwo vertically differentiated exhibition areas in two major industries, with over 120 manufacturing industry products, highlighting strong interaction, multi interaction, and immersive scene experiences, promoting the display and trading of innovative achievements in laser and digital manufacturing.
Full session 2023 Optoelectronic Technology Expo
2023.8.28-30 | Shenzhen Futian Convention and Exhibition Center

Long press the QR code to register immediately and directly reach the venue